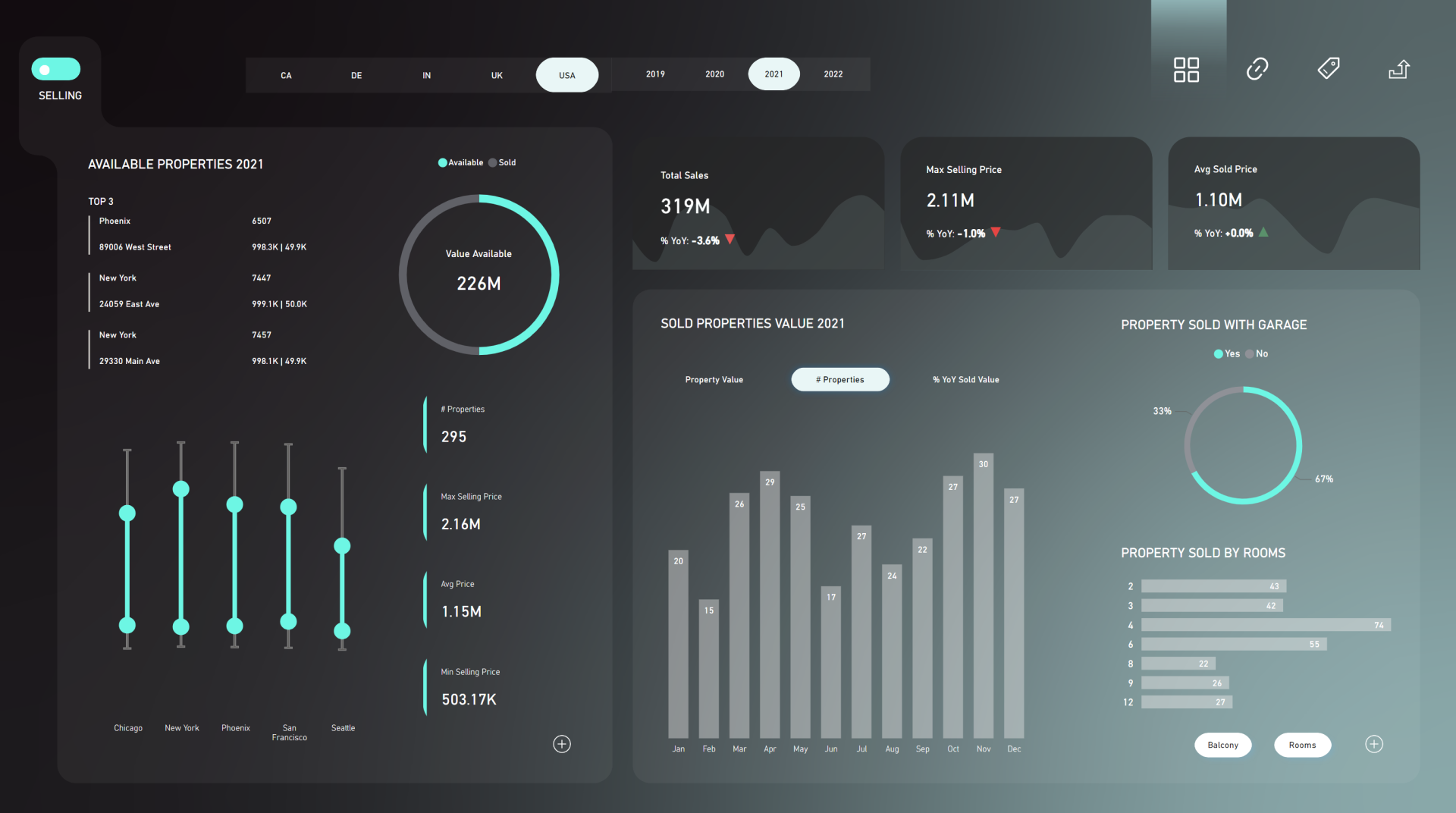
1. Start by Understanding the Problem
Every great report starts with a clear understanding of the problem it’s trying to solve. A report without a clear purpose often becomes part of the “unused reports pile”. Your first task is to
clarify the problem and its significance.
Ask yourself:
- What problem are we solving?
- Why does this problem matter to business?
Understanding the problem also means recognizing the value your report will create.
This value might involve:
- Increasing revenue
- Reducing cost
- Saving time
- Finding opportunities for growth
Beyond identifying the problem, define the who and the what:
- Who will use this report? A CEO, senior managers, or operational teams?
- What decisions will it support?
Document these details clearly to set the foundation for your project. Define the goals, the problem, and the value, and break them down into specific decisions the report will help make. This clarity will guide your work and align everyone involved.
Example:
A company wants to know which product categories to expand. The problem isn’t just about identifying sales trends - it’s about forecasting which categories offer the highest growth potential. A report addressing this must focus on actionable insights, not just raw data.
2. Engage Stakeholders Early and Often
Stakeholders hold the business knowledge you need to create a meaningful report. Their input ensures that your work aligns with the organization’s goals and solves the right problems. As a developer, your technical expertise is essential, but without their insights,
it’s easy to miss the mark.
Key
Steps:
- Identify stakeholders
- Communicate regularly
- Listen to feedback
Stakeholders might include:
- End users who rely on the report
- Subject matter experts who understand the data
- Project managers overseeing the broader initiative
Don’t wait until the report is finished to involve them. Engage stakeholders from the beginning and throughout the process. This approach:
- Improve understanding of the business problem
- Incorporates valuable feedback and ensures the report aligns with their needs
- Builds buy-in - when stakeholders are involved, they feel ownership and are more likely to embrace the final product
Engaging stakeholders builds trust and ensures the report meets their needs.
Tip:
Don’t treat the initial requirements as set in stone. Use stakeholder feedback to refine and improve the report throughout the development process.
3. Adopt an Iterative Approach
Reports rarely turn out perfect on the first try. It’s tempting to aim for a polished report from the start, but this approach often leads to missed opportunities and wasted effort. By working iteratively, you can refine the report based on feedback and ensure it evolves to meet business needs.
Here’s how iteration works:
- Start with a simple prototype - a basic version of the report that covers the core functionality
- Share the prototype with stakeholders to gather feedback
- Refine and expand the report based on their input
- Be open to changes, even if they deviate from the original plan
This process not only speeds up development but also results in a report that better reflects the organization’s needs. Iteration allows flexibility, helping you adjust as new insights emerge, and ensures the final product is far superior to what you might have envisioned initially.
Example:
Imagine you start with a simple bar chart showing sales by region. After feedback, you realize stakeholders want to drill down into individual sales representatives’ performance. Iteration allows you to add this functionality and deliver a more useful report.

4. Promote Your Report
Creating a great report is only half the battle - you also need to make sure people use it. Even the most well-designed report can fail to deliver value if it remains unnoticed or unused. Promoting your report is about ensuring it reaches the right people, resonates with them, and integrates into their decision-making processes.
Here’s how to promote your report effectively:
- Host training sessions or workshops to explain how the report works and why it’s useful
- Use communication channels like email, Teams, or Slack to share key details about the report
- Highlight the value and impact of the report to make it clear why it matters, focus on the impact it will have
Create supporting materials:
- Short introductory videos (5–15 minutes) explaining what the report does, how to use it, and its key features
- Quick start guides or infographics showing where to find the report and how to interact with it
When you promote your report, you’re not just sharing information - you’re building excitement and ensuring it gets the attention it deserves.
Engagement Tips:
Tailor your communication style and content to different audiences. For example, a CEO might care more about high-level insights, while operational teams will want detailed, actionable data. Share success stories, showcase examples of how the report has already delivered value to encourage others to adopt it.

5. Educate Your Users
Don’t assume everyone knows how to use Power BI. While many users are comfortable with tools like Excel, Power BI introduces unique features that might be unfamiliar. Without proper education, even the most intuitive report can leave users feeling overwhelmed or confused. Education is the bridge that helps users confidently navigate and extract value from your report.
To ensure users can get the most out of your report:
- Provide training on key features, like drill-through, bookmarks, and slicers
- Demonstrate how to filter and customize the report to meet individual needs
- Explain how to interpret key metrics and visualizations
- Create step-by-step guides on navigating the report
If you’re handing over the report to a client, make sure their team is equipped to maintain it. Training both end users and in-house developers ensures the report remains valuable long after delivery.
Hope you like it!
Give it a try and see how it works for you! I’d love to hear what you think or see how you use this in your own reports.